We put the Sony Xperia 1 IV through our rigorous DXOMARK Camera test suite to measure its performance in photo, video, and zoom quality from an end-user perspective. This article breaks down how the device fared in a variety of tests and several common use cases and is intended to highlight the most important results of our testing with an extract of the captured data.
Overview
Key camera specifications:
- Primary: 12MP 1/1.7-inch sensor, 1.8 μm pixels, f/1.7-aperture lens with 24mm equivalent focal length, PDAF, OIS
- Ultra-wide: 12MP 1/2.5-inch sensor, f/2.2-aperture lens with 16mm equivalent focal length
- Tele: 12MP 1/3.5-inch sensor, variable focal length from 85-125mm equivalent, f/2.3-f/2.8 aperture, OIS
- Video: 4K video at 24, 25, 30, 60 and 120fps, HDR
Scoring
Sub-scores and attributes included in the calculations of the global score.
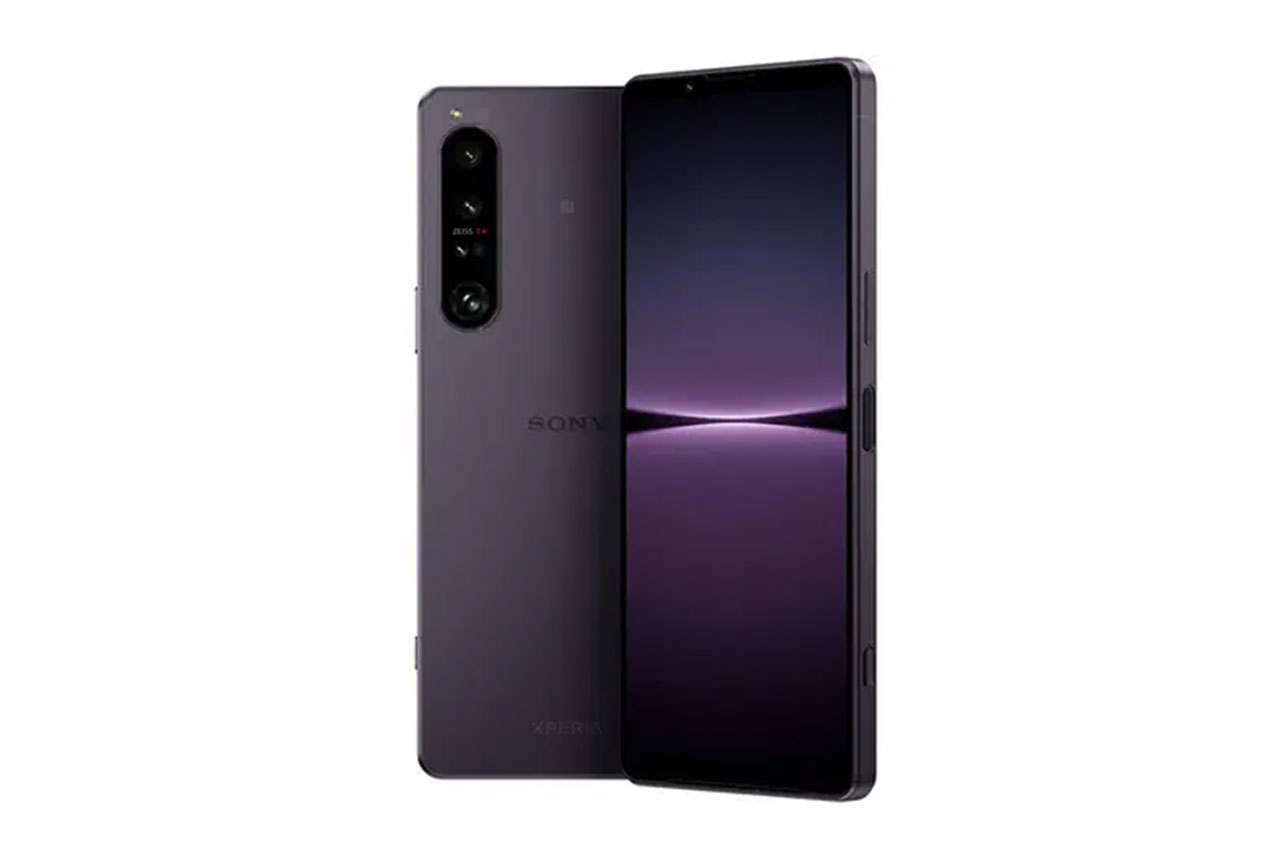

Sony Xperia 1 IV


Use cases & Conditions
Use case scores indicate the product performance in specific situations. They are not included in the overall score calculations.
Outdoor
Photos & videos shot in bright light conditions (≥1000 lux)
Indoor
Photos & videos shot in good lighting conditions (≥100lux)
Lowlight
Photos & videos shot in low lighting conditions (<100 lux)
Friends & Family
Portrait and group photo & videos
 111th
111th 79th
79thCons
- Limited dynamic range
- Ringing artifacts
- Unnatural skin tones in daylight
- Exposure and white balance instabilities in video
- Strong underexposure in some night portraits
- Low contrast at long-range tele, lack of detail at all zoom settings
With a DXOMARK Camera score of 118, the Sony Xperia 1 IV delivered a fairly balanced performance in our tests, achieving decent results in photo, zoom and video when the light conditions were not too difficult. However, it could not quite match the best rivals in the Ultra-Premium price segment.
In photo mode, the camera generally captured nice pictures, with good exposure and natural texture rendering. The device’s tele lens with a variable focal length from 85-125mm (35mm-equivalent) is a stand-out feature and delivered good results in our tests, making tele zoom capture the Sony’s strong point. In video mode, our testers liked the accurate and smooth autofocus, as well as the decent video stabilization.
Apart from the more sophisticated tele zoom setup, the Xperia 1 IV’s camera hardware is mostly identical to its in-house rival Xperia 5 IV. This said, despite the similar camera specifications, overall image quality and camera performance were not quite the same and the Xperia 1 IV’s overall score is one point lower than the Xperia 5 IV. Differences were mainly noticeable in color and autofocus where the Xperia 5 IV delivered better results. On the other hand, the flagship Xperia 1 IV was better in the zoom category.
Portrait shots captured with the Sony showed good exposure in all conditions and the camera recorded sharp detail in bright light. A wide depth of field ensured good sharpness on subjects in different focus planes in group shots. Skin tones could look a little unnatural, though, especially in daylight shooting, and our testers also observed slight motion blur and fusion artifacts on moving subjects.
The Sony Xperia 1 IV camera did a good job in low-light scenes, capturing fairly good detail and good exposure. However, a limited dynamic range resulted in shadow and highlight clipping, and image noise was often noticeable. The camera did struggle slightly more in video mode where the dynamic range was slightly more limited than for photos, and luminance noise crept into the frame. Color was pleasant and warm both in photo and video, but white balance instabilities were sometimes noticeable when recording video.
Test summary
About DXOMARK Camera tests: DXOMARK’s Camera evaluations take place in laboratories and in real-world situations using a wide variety of subjects. The scores rely on objective tests for which the results are calculated directly by measurement software on our laboratory setups, and on perceptual tests in which a sophisticated set of metrics allow a panel of image experts to compare aspects of image quality that require human judgment. Testing a smartphone involves a team of engineers and technicians for about a week. Photo, Zoom, and Video quality are scored separately and then combined into an Overall score for comparison among the cameras in different devices. For more information about the DXOMARK Camera protocol, click here. More details on smartphone camera scores are available here. The following section gathers key elements of DXOMARK’s exhaustive tests and analyses. Full performance evaluations are available upon request. Please contact us on how to receive a full report.
Photo
Sony Xperia 1 IV
169
For scoring and analysis, DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2,600 test images both in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The photo protocol is designed to take into account the main use cases and is based on typical shooting scenarios, such as portraits, family, and landscape photography. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting images against a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements on images of charts captured in the lab under different lighting conditions from 1 to 1,000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
The Sony Xperia 1 IV is a decent smartphone option for still image capture, but it did not match the best in class in our tests. It produced good exposure and captured good detail in most conditions, but dynamic range was limited, resulting in highlight and/or shadow clipping in difficult high-contrast scenes. Our testers also observed some instabilities and found the preview image to not always be reliable. Overall, image quality was quite close to the Xperia 5 IV which is not a surprise given that, apart from the tele module, both devices use the same camera hardware. Differences between the two cameras were mainly visible in terms of exposure and color.
Close-Up
Close-up shots taken with the Sony 1 IV showed strong corner softness. Images were also out of focus and not really sharp at the center of the frame either. Therefore, the Sony Xperia 1 IV did not qualify for our full macro image quality analysis.

Exposure
Sony Xperia 1 IV
130
Exposure is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The main attribute evaluated is the brightness of the main subject through various use cases such as landscape, portrait, or still life. Other factors evaluated are the contrast and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Repeatability is also important because it demonstrates the camera's ability to provide the same rendering when shooting several images of the same scene.
In our tests, the Xperia 1 IV produced acceptable exposure in all shooting conditions, but a lack of dynamic range meant that we saw some clipping that was usually more noticeable in the highlight portions of the frame than in the shadows. Compared with the Xperia 5 IV, exposure was quite similar, but the dynamic range limitations were slightly more noticeable.
In high-contrast scenes, such as the one below, the Xperia 1 IV changed exposure behavior slightly. In this kind of condition, clipping was more noticeable in the shadow areas than in the highlights, resulting in underexposed foreground subjects. In comparison, the Xperia 5 IV maintained better subject exposure while producing more clipped highlights in the brighter background.

Color
Sony Xperia 1 IV
130
Color is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The image quality attributes analyzed are skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, and repeatability. For color and skin tone rendering, we penalize unnatural colors but we respect a manufacturer's choice of color signature.
Color performance on the Xperia 1 IV was decent but left some room for improvement. When shooting in daylight conditions, a pinkish color cast was often noticeable. Under other types of lighting, the color response tended to be slightly warm but pleasant.
In addition to the pinkish cast mentioned above, in some daylight portrait shots skin-tone rendering was unnatural.

Autofocus
Sony Xperia 1 IV
125
Autofocus tests concentrate on focus accuracy, focus repeatability, shooting time delay, and depth of field. Shooting delay is the difference between the time the user presses the capture button and the time the image is actually taken. It includes focusing speed and the capability of the device to capture images at the right time, what is called 'zero shutter lag' capability. Even if a shallow depth of field can be pleasant for a single subject portrait or close-up shot, it can also be a problem in some specific conditions such as group portraits; Both situations are tested. Focus accuracy is also evaluated in all the real-life images taken, from infinity to close-up objects and in low light to outdoor conditions.
In our testing, the Sony Xperia 1 IV autofocus was a little slower and less consistent than on some rivals. Our testers measured quite a long delay between pressing the shutter and the actual capture. While focus locked on precisely most of the time, a variation in focus time was quite noticeable in low light and under indoor conditions. We also noticed slight focus inaccuracies in some high-contrast shots.
Depth of field was wider on the Sony Xperia 1 IV than on the Google Pixel 7, allowing for better sharpness on subjects that were located further back in the scene. This can be an advantage in group portraits.

Texture
Sony Xperia 1 IV
125
Texture tests analyze the level of details and the texture of subjects in the images taken in the lab as well as in real-life scenarios. For natural shots, particular attention is paid to the level of details in the bright and dark areas of the image. Objective measurements are performed on chart images taken in various lighting conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The charts used are the proprietary DXOMARK chart (DMC) and the Dead Leaves chart.
Photos captured in bright daylight showed good texture, but compared to the Xperia 5 IV and Pixel 7 some loss of detail was noticeable. Our testers also observed a loss of detail in high-contrast scenes and in low light, but texture rendering remained natural across all light conditions.

Noise
Sony Xperia 1 IV
117
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure on real-life images as well as images of charts taken in the lab. For natural images, particular attention is paid to the noise on faces, landscapes, but also on dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Noise on moving objects is also evaluated on natural images. Objective measurements are performed on images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The chart used is the Dead Leaves chart and the standardized measurement such as Visual Noise derived from ISO 15739.
Image noise was somewhat more noticeable on the Xperia 1 IV than on some rivals. Luminance noise was usually visible in all conditions, especially in areas of plain color. We also observed some of the more intrusive chromatic noise when shooting under indoor conditions or in low light. Overall, the Xperia 1 IV behaved the same as the Xperia 5 IV in terms of noise control.

Artifacts
Sony Xperia 1 IV
82
The artifacts evaluation looks at lens shading, chromatic aberrations, geometrical distortion, edges ringing, halos, ghosting, quantization, unexpected color hue shifts, among others type of possible unnatural effects on photos. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction on the score. The main artifacts observed and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Ringing and color quantization were the most noticeable image artifacts on the Xperia 1 IV. Ringing was often visible on high-contrast edges, for example around objects in front of a brighter background, especially when shooting indoors or in low light. Our testers also reported some ghosting and fusion artifacts when shooting moving subjects. In some images, we also saw a slight lack of sharpness around the edges of the frame.
Bokeh
Sony Xperia 1 IV
85
Bokeh is tested in one dedicated mode, usually portrait or aperture mode, and analyzed by visually inspecting all the images captured in the lab and in natural conditions. The goal is to reproduce portrait photography comparable to one taken with a DLSR and a wide aperture. The main image quality attributes paid attention to are depth estimation, artifacts, blur gradient, and the shape of the bokeh blur spotlights. Portrait image quality attributes (exposure, color, texture) are also taken into account.
The Sony’s bokeh mode is overall very similar to the Sony Xperia 5 IV’s mode. It produced nice images with a natural blur gradient. In addition, spotlights in the background were rendered in a natural way. However, our testers observed some unwanted artifacts at the transition from blurred to sharp areas of the image. These artifacts occurred unexpectedly and did not follow a specific pattern, reducing the overall quality of the blur effect. Moreover, colors were not always true to reality, especially in indoor light conditions.
The Xperia 1 IV blurs the parts of the scene between camera and main subject, not just the background. While this is a good thing, the foreground blur gradient was not always smooth and natural.
Dynamic range was quite drastically reduced in bokeh mode compared to standard photo mode. In this backlit scene, the bright background was noticeably more clipped in the bokeh mode image.
Preview
Sony Xperia 1 IV
93
Preview tests analyze the image quality of the camera app's preview of the image, with particular attention paid to the difference between the capture and the preview, especially regarding dynamic range and the application of the bokeh effect. Also evaluated is the smoothness of the exposure, color, and focus adaptation when zooming from the minimal to the maximal zoom factor available. The preview frame rate is measured using the LED Universal Timer.
The preview image showed several differences to the final capture, the main one being exposure. In high-contrast scenes, highlight clipping was noticeably stronger in the preview image.
Zoom
Sony Xperia 1 IV
169
DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate over 400 test images in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor, and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings and pinch zoom at various zoom factors from ultra wide to very long-range zoom. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting the images against a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements of chart mages captured in the lab under different conditions from 20 to 1000 lux and color temperatures from 2300K to 6500K.
The Sony Xperia 1 IV comes with a 16mm ultra-wide camera. In our tests, the Sony’s ultra-wide images showed a slight loss of detail and, like the primary camera, a limited dynamic range. Noise was noticeable in most shots but overall fairly well under control – higher than the Xperia 5 IV in daylight, but lower in low light.
At tele zoom settings, the Sony Xperia 1 IV did a good job at preserving detail, scoring better than both the Xperia 5 IV and the Google Pixel 7. The device’s longer tele allows it to preserve more detail than the Xperia 5 IV at medium and long range. On the other hand, at close range, texture looks less natural and most detail is lost.
Video Zoom
The Xperia 1 IV does not support the pinch zoom gesture for switching between the ultra-wide primary and tele camera modules, offering zoom buttons only. This makes changing zoom levels slightly uncomfortable. In video mode, the jumps between cameras were quite noticeable, with a change in texture and color between camera modules.

Wide
Sony Xperia 1 IV
122
These tests analyze the performance of the ultra-wide camera at several focal lengths from 12 mm to 20 mm. All image quality attributes are evaluated, with particular attention paid to such artifacts as chromatic aberrations, lens softness, and distortion. Pictures below are an extract of tested scenes.
When shooting with the ultra-wide camera, slight noise was often visible but detail was overall rendered fairly nicely.

Tele
Sony Xperia 1 IV
128
All image quality attributes are evaluated at focal lengths from approximately 40 mm to 300 mm, with particular attention paid to texture and detail. The score is derived from a number of objective measurements in the lab and perceptual analysis of real-life images.
At close range, the Xperia 1 IV images showed a considerable loss of detail compared to its rivals in this test. This is because in close range, the Xperia 1 IV is still using its primary camera and performs a digital zoom into the frame, whereas the Xperia 5 IV already switched to its tele module.
However, when shooting at a long range, images showed better detail than the Xperia 5 IV and the Google Pixel 7. A lack of contrast was noticeable, though.
Video
Sony Xperia 1 IV
159
DXOMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2.5 hours of video in controlled lab environments and in natural low-light, indoor and outdoor scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The evaluation consists of visually inspecting natural videos taken in various conditions and running objective measurements on videos of charts recorded in the lab under different conditions from 1 to 1000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
The Xperia 1 IV’s video mode offered a smooth and accurate autofocus as well as effective video stabilization. Our testers also found detail to be quite sharp when recording in bright light but, like for still images, dynamic range was limited, resulting in highlight and shadow clipping. We also saw some exposure and white balance instabilities.

Exposure
Sony Xperia 1 IV
116
Exposure tests evaluate the brightness of the main subject and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Stability and temporal adaption of the exposure are also analyzed.
Like in photo mode, the camera’s dynamic range was quite limited when shooting video. Subject exposure was accurate but the exposure often oscillated in daylight and under consistent indoor lighting. These instabilities resulted in highlight clipping in the sky, as can be seen in the sample below.

Color
Sony Xperia 1 IV
120
Image-quality color analysis looks at color rendering, skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, stability of the white balance and its adaption when light is changing.
The Sony Xperia 1 IV captured quite pleasant color in video mode, despite the occasional appearance of a slight pink or blue cast in bright light. A warm white balance was noticeable in low light and under indoor conditions. The effect was mostly pleasant but could be too strong in very low light.

Autofocus
Sony Xperia 1 IV
120
The Xperia 1 IV’s video autofocus performance was quite consistent, usually without any instabilities. In addition, focus transitions were generally quite smooth.

Texture
Sony Xperia 1 IV
118
Texture tests analyze the level of details and texture of the real-life videos as well as the videos of charts recorded in the lab. Natural videos recordings are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the level of details in the bright and areas as well as in the dark. Objective measurements are performed of images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The charts used are the DXOMARK chart (DMC) and Dead Leaves chart.
In our texture tests, the Xperia 1 IV tended to provide better detail than the Xperia 5 IV in perceptual real-life scenes but that was not always the case for objective lab measurements, depending on the test setup used. In this sample scene, the Xperia 1 IV captured better subject detail. This said, despite the sharper edge detail, the texture was not as detailed as on the Google Pixel 7.

Noise
Sony Xperia 1 IV
120
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure, temporal aspects on real-life video recording as well as videos of charts taken in the lab. Natural videos are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the noise in the dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Objective measurements are performed on the videos of charts recorded in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The chart used is the DXOMARK visual noise chart.
Luminance noise was generally well controlled in videos but became more intrusive as the lights were dimmed. In indoor and low light conditions, the Xperia 1 IV’s target exposure was also lower than with the Google Pixel 7, which explains the Sony’s lower noise levels and the Pixel 7’s lower noise score.

Stabilization
Sony Xperia 1 IV
119
Stabilization evaluation tests the ability of the device to stabilize footage thanks to software or hardware technologies such as OIS, EIS, or any others means. The evaluation looks at residual motion, smoothness, jello artifacts and residual motion blur on walk and run use cases in various lighting conditions. The video below is an extract from one of the tested scenes.
Video stabilization was very effective, resulting in smooth frame motion when walking or running while recording. However, some sharpness differences between frames were noticeable. When hand-holding the device in a static position, hand movements were counteracted effectively.

Artifacts
Sony Xperia 1 IV
86
Artifacts are evaluated with MTF and ringing measurements on the SFR chart in the lab as well as frame-rate measurements using the LED Universal Timer. Natural videos are visually evaluated by paying particular attention to artifacts such as aliasing, quantization, blocking, and hue shift, among others. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction from the score. The main artifacts and corresponding point loss are listed below.
The Xperia 1 IV did a good job at managing video artifacts. Our testers noticed a judder effect that was mostly visible during panning movements, quite frequent ringing, and aliasing on fine detail in pretty much all conditions.






































DXOMARK encourages its readers to share comments on the articles. To read or post comments, Disqus cookies are required. Change your Cookies Preferences and read more about our Comment Policy.