We put the Huawei Mate 60 Pro through our rigorous DXOMARK Display test suite to measure its performance across six criteria. In this test results, we will break down how it fared in a variety of tests and several common use cases.
Overview
Key display specifications:
- 6.82 inches OLED (~89.4% screen-to-body ratio)
- Dimensions: 163.6 x 79.0 x 8.1 mm (6.44 x 3.11 x 0.32 inches)
- Resolution: 1260 x 2720 pixels, (~440 ppi density)
- Aspect ratio: 19.5:9
- Refresh rate: 120 Hz
Scoring
Sub-scores and attributes included in the calculations of the global score.
 Huawei Mate 60 Pro
Huawei Mate 60 Pro

143
display
143
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
Best: Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos) (163)
163
Google Pixel 8 Pro
Best: Google Pixel 8 Pro (164)
136
Samsung Galaxy S23
Best: Samsung Galaxy S23 (162)
117
Honor Magic6 Pro
Best: Honor Magic6 Pro (159)
167
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
Best: Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos) (170)
123
OnePlus Open
Best: OnePlus Open (163)
Position in Global Ranking

27
th
2. Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
155
3. Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
154
3. Samsung Galaxy S24 (Exynos)
154
7. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold5
152
11. Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max
149
11. Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
149
11. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip5
149
16. Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra
148
23. Apple iPhone 13 Pro Max
145
28. Samsung Galaxy A55 5G
141
30. Honor Magic4 Ultimate
140
43. Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
136
46. Samsung Galaxy S22+ (Exynos)
135
51. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip4
134
51. Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Exynos)
134
51. Samsung Galaxy A35 5G
134
51. Vivo X80 Pro (MediaTek)
134
58. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4
133
58. Samsung Galaxy S22 (Snapdragon)
133
58. Samsung Galaxy S22 (Exynos)
133
58. Vivo X80 Pro (Snapdragon)
133
65. Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G (Snapdragon)
131
65. Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
131
69. Samsung Galaxy S21 FE 5G (Snapdragon)
130
76. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold3 5G
129
76. Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Snapdragon)
129
85. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip3 5G
128
85. Samsung Galaxy S23 FE
128
85. Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
128
90. Apple iPhone 12 Pro Max
127
97. Vivo X70 Pro (MediaTek)
125
97. Vivo X60 Pro 5G (Snapdragon)
125
113. Oppo Reno6 Pro 5G (Snapdragon)
123
113. Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
123
113. Xiaomi Redmi Note 13 Pro Plus 5G
123
118. Apple iPhone SE (2022)
122
118. Motorola Edge 30 Pro
122
124. Samsung Galaxy A54 5G
120
128. Motorola Edge 40 Pro
118
131. Motorola Razr 40 Ultra
117
135. Apple iPhone 11 Pro Max
116
140. Motorola Edge 20 Pro
111
140. Samsung Galaxy A52 5G
111
144. Samsung Galaxy A52s 5G
110
150. Xiaomi Redmi K50 Gaming
107
152. Nubia RedMagic 6 Pro
105
153. Samsung Galaxy A53 5G
104
161. Microsoft Surface Duo
99
163. Nubia RedMagic 7 Pro
97
164. Xiaomi Mi 10T Pro 5G
95
172. Samsung Galaxy A22 5G
74
173. Xiaomi Black Shark 3 Pro
69
175. Lenovo Legion Phone 2 Pro
60
Position in Ultra-Premium Ranking

23
rd
2. Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
155
3. Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
154
5. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold5
152
9. Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max
149
9. Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
149
9. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip5
149
14. Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra
148
20. Apple iPhone 13 Pro Max
145
25. Honor Magic4 Ultimate
140
34. Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
136
36. Samsung Galaxy S22+ (Exynos)
135
39. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip4
134
39. Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Exynos)
134
39. Vivo X80 Pro (MediaTek)
134
44. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold4
133
44. Vivo X80 Pro (Snapdragon)
133
48. Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G (Snapdragon)
131
48. Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
131
55. Samsung Galaxy Z Fold3 5G
129
55. Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Snapdragon)
129
59. Samsung Galaxy Z Flip3 5G
128
59. Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
128
63. Apple iPhone 12 Pro Max
127
74. Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
123
80. Motorola Razr 40 Ultra
117
81. Apple iPhone 11 Pro Max
116
85. Microsoft Surface Duo
99
88. Xiaomi Black Shark 3 Pro
69
Pros
- Color rendering is accurate in most ambient lighting environments
- Touch is fluid, accurate, and responsive
- Readability is comfortable in most ambient lighting environments
Cons
- Lacks details under sunlight
- Long stutters and aliasing when playing video games
- Lack of brightness and details in the darkest areas when watching HDR10 videos
The Huawei Mate 60 Pro’s display provides a very satisfying user experience overall, achieving a global score that was a couple of points higher than its predecessor, the Mate 50 Pro. The latest version’s screen showed notable improvements in the motion and touch attributes as well as in artifacts management.
The screen’s readability generally maintained the same level as its predecessor, although low-light readability lacked some necessary brightness. We noted that the device’s brightness at midnight was less intense than the screen brightness activated in low light during the day, presumably to prevent dazzling users’ eyes with strong light in the dark. Readability outdoors, however, was quite good, with screen brightness reaching a peak of more than 1700 nits (while its predecessor did not trigger maximum brightness in our bench).
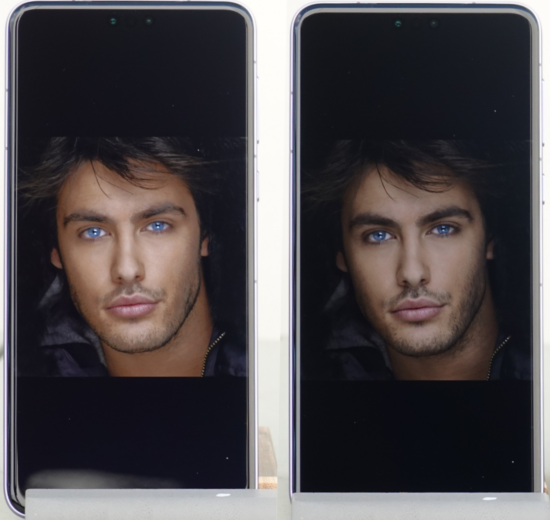
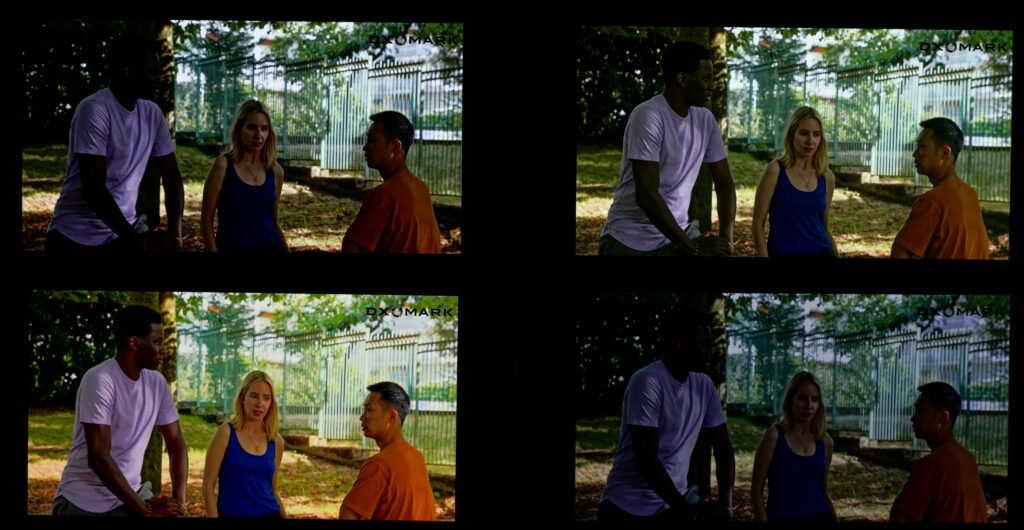
The device also has an option called “HDR Images” that is on by default, which enhances “the display quality of high dynamic range images.” This enhancement also is applied to non-HDR images, like our patterns. A comparison is shown below (shades lighting environment). When the HDR Images option is on, the content appears more readable, but the rendering loses details in the darkest shades, and the subject’s face appears flatter.
HDR on, left; HDR off, right.
Screen color remains a strong point of the Mate 60 Pro’s display, even though a purple tint cast was noticed when viewing photos.
While motion on the Mate 60 Pro was much improved from the Mate 50 Pro, the screen still tended to drop frames when playing video games.
Finally, touch interactions were smooth, pleasing, with a very fast reaction time.
Test summary
About DXOMARK Display tests: For scoring and analysis in our smartphone and other display reviews, DXOMARK engineers perform a variety of objective and perceptual tests under controlled lab and real-life conditions. Note that we evaluate display attributes using only the device’s built-in display hardware and its still image (gallery) and video apps at their default settings. (For in-depth information about how we evaluate smartphone and other displays, check out our articles, “How DXOMARK tests display quality” and “A closer look at DXOMARK Display testing.”
The following section gathers key elements of our exhaustive tests and analyses performed in DXOMARK laboratories. Detailed performance evaluations under the form of reports are available upon request. Do not hesitate to contact us.
Readability
143
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
How Display Readability score is composed
Readability evaluates how easily and comfortably users can read still content (photos & web) on the display under different real-life conditions. DXOMARK uses its Display Bench to recreate ambient light conditions ranging from total darkness to bright sunlight. In addition to laboratory tests, perceptual analysis is also made in real-life environments.
Luminance under various lighting conditions
Readability in an indoor (1000 lux) environment
From left to right: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
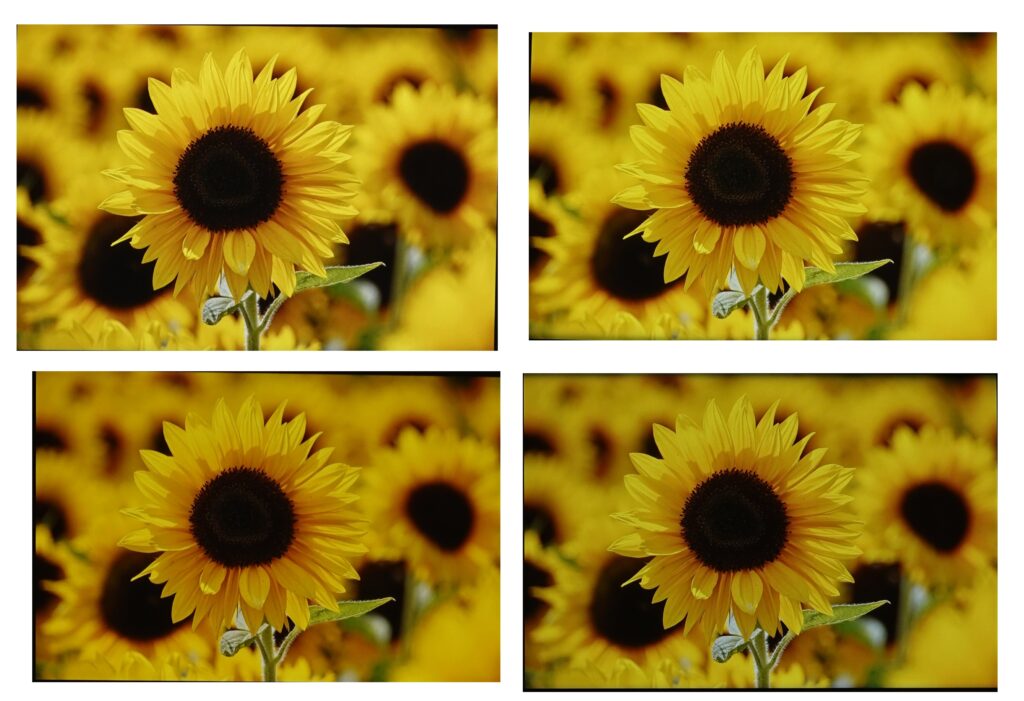
Readability in an outdoor (20 000 lux) environment
From left to right: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
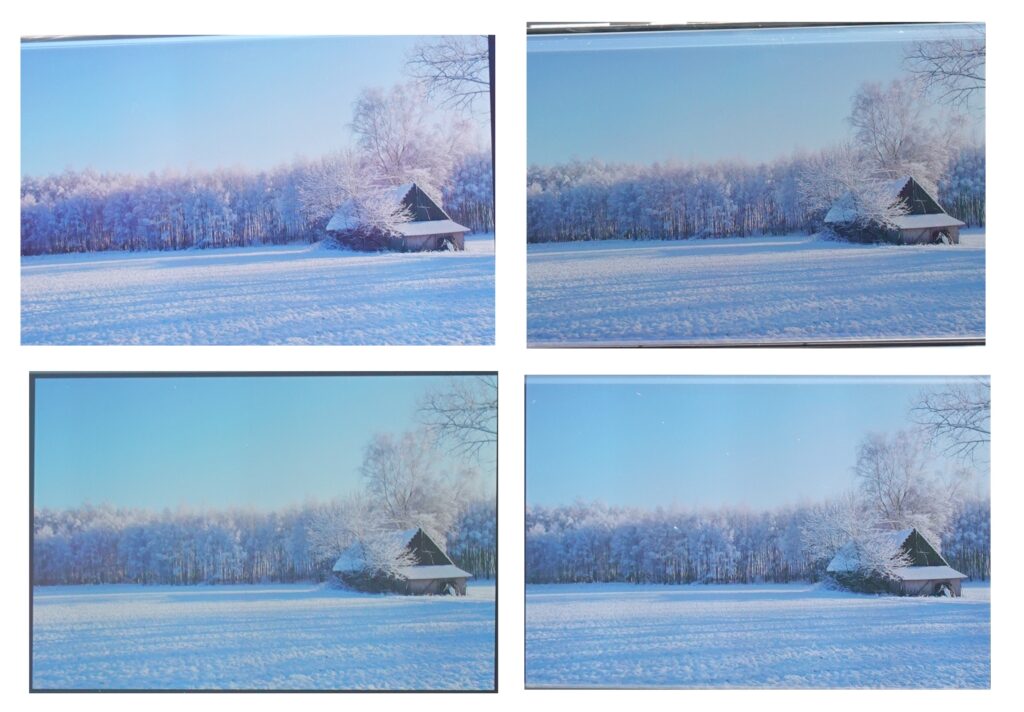
Readability in a sunlight (>90 000 lux) environment
From left to right: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
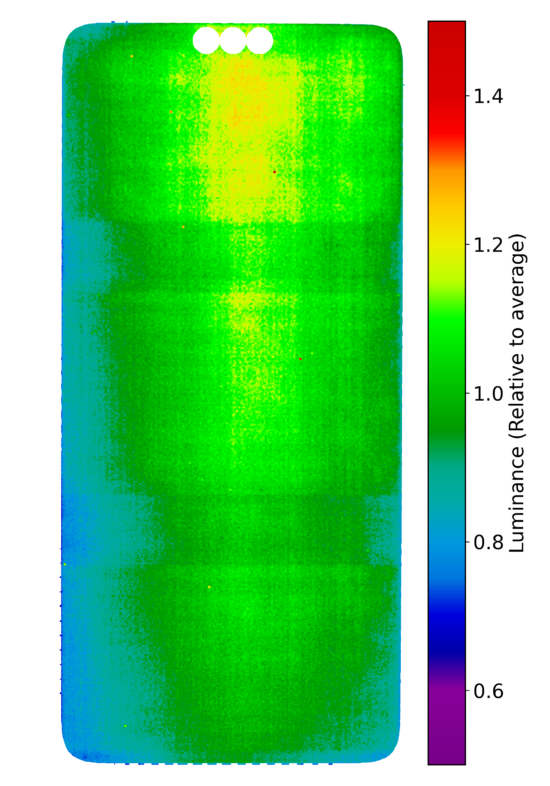
Luminance uniformity measurement
This graph shows the uniformity of the display with a 20% gray pattern. The more visible the green color, the more uniform the display.
Color
163
Google Pixel 8 Pro
Google Pixel 8 Pro
How Display Color score is composed
The color attribute evaluates the capacity of the device to accurately reproduce colors. The measurements taken are for fidelity, white point color, and gamut coverage. We perform color evaluations for different lighting conditions to see how well the device can manage color in the surrounding environment. Colors are measured using a spectrophotometer in a controlled lighting environment. Perceptual analysis of color rendering is against the reference pattern displayed on a calibrated professional monitor.
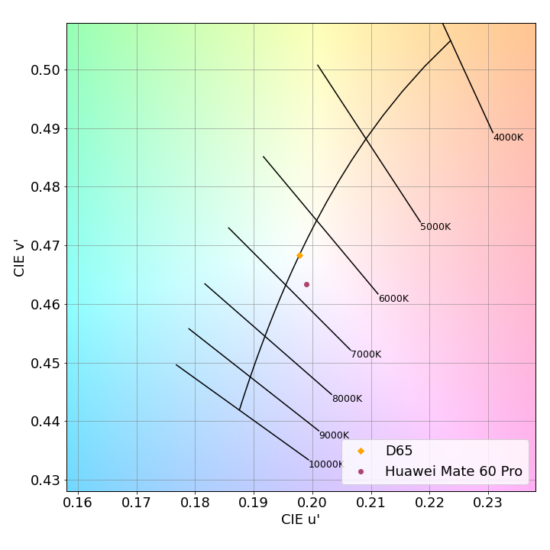
White point under D65 illuminant at 1000 lux
Color rendering indoors (1000 lux)
Clockwise from top left: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
Color rendering in sunlight (>90 000 lux)
Clockwise from top left: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
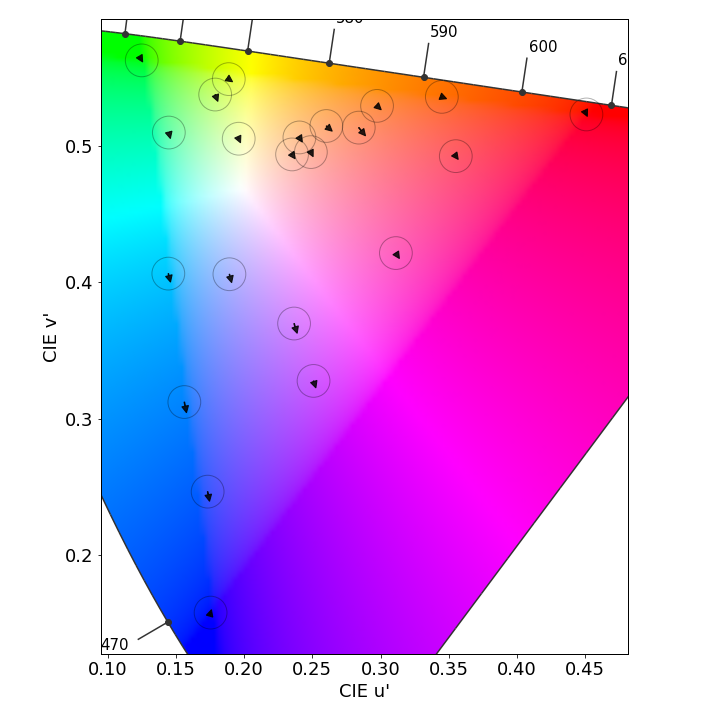
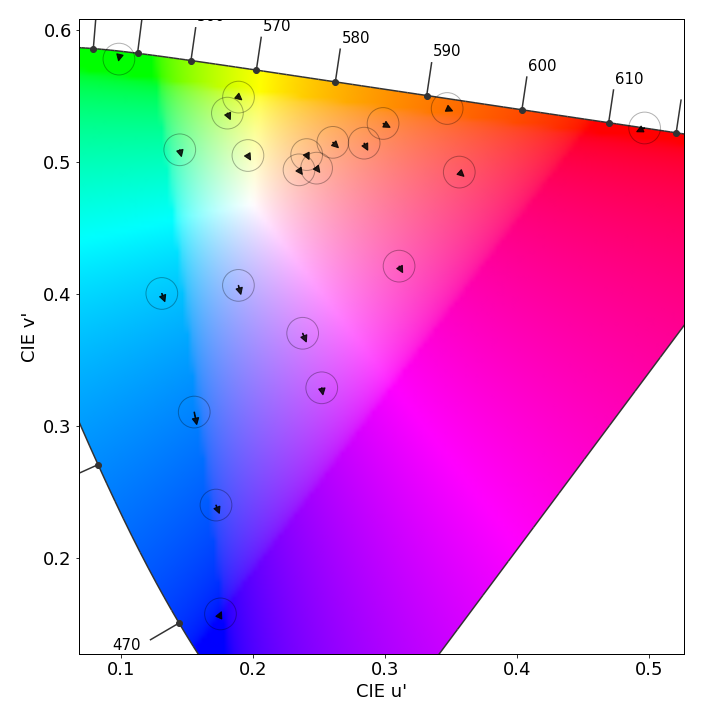
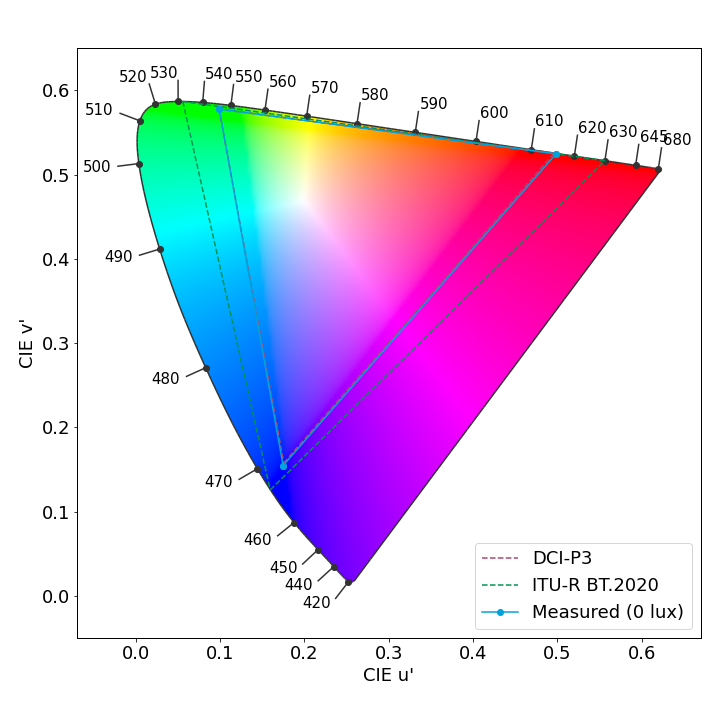
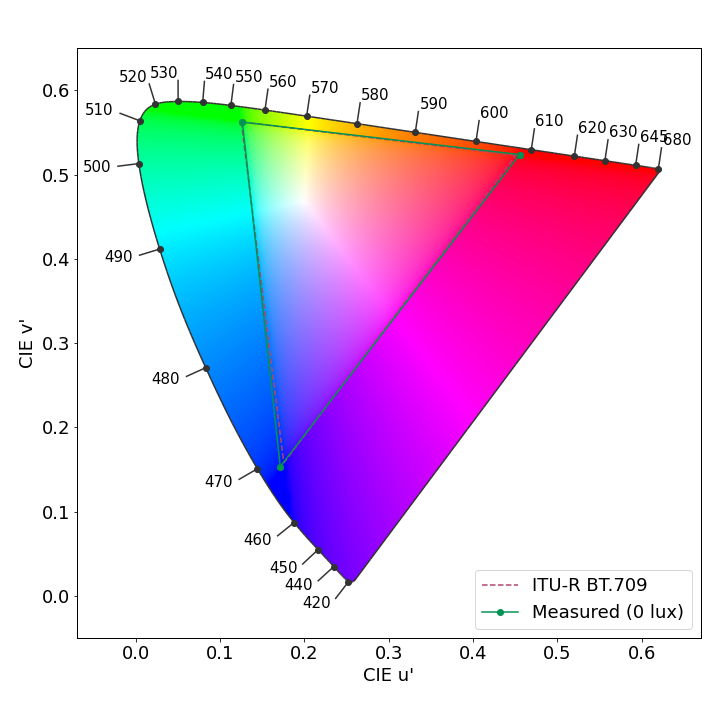
Color fidelity measurements
Huawei Mate 60 Pro, color fidelity at 1000 lux in the sRGB color space
Huawei Mate 60 Pro, color fidelity at 1000 lux in the Display-P3 color space
Each arrow represents the color difference between a target color pattern (base of the arrow) and its actual measurement (tip of the arrow). The longer the arrow, the more visible the color difference is. If the arrow stays within the circle, the color difference will be visible only to trained eyes.
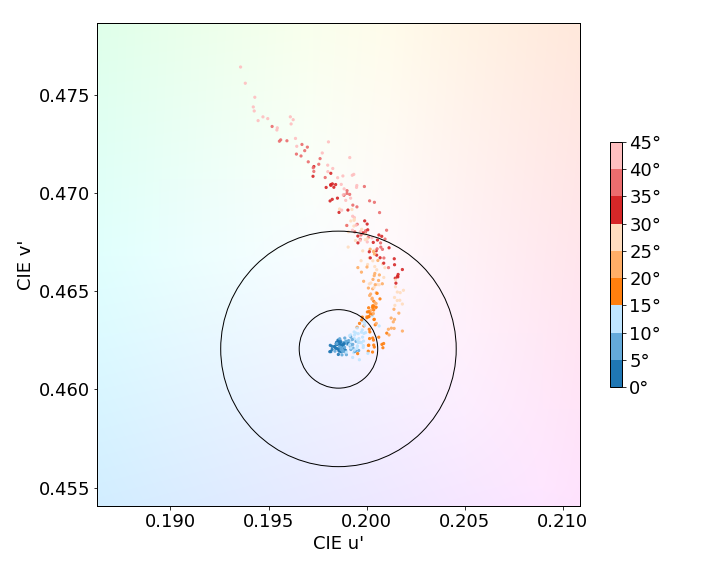
Color behavior on angle
This graph shows the color shift when the screen is at an angle. Each dot represents a measurement at a particular angle. Dots inside the inner circle exhibit no color shift in angle; those between the inner and outer circle have shifts that only trained experts will see; but those falling outside the outer circle are noticeable.
Color shift on angle

From left to right: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
Video
136
Samsung Galaxy S23
Samsung Galaxy S23
How Display Video score is composed
Our video attribute evaluates the Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) and High Dynamic Range (HDR10) video handling of each device in indoor and low-light conditions. We measure tone mapping, color gamut, brightness and contrast of the display. We perform perceptual analysis against our professional reference monitor (Sony BVM-HX310) to ensure that the rendering respects the artistic intent.
Video brightness at 10% APL in the dark ( < 5 lux)
Video rendering in a low-light (0 lux) environment
Clockwise from top left: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
Clockwise from top left: Huawei Mate 60 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro, Oppo Find X6 Pro, Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max.
(Photos for illustration only)
Gamut coverage for video content
The primary colors are measured both in HDR10 and SDR. The extracted color gamut shows the extent of the color area that the device can render. To respect the artistic intent, the measured gamut should match the master color space of each video.
Motion
117
Honor Magic6 Pro
Honor Magic6 Pro
How Display Motion score is composed
The motion attribute evaluates the handling of dynamic contents. Frame drops, motion blur, and playback artifacts are scrutinized using games and videos.
Video frame drops
These long exposure photos present the number of frame irregularities in a 30-second video. A good performance shows a regular pattern (either a flat gray image or a pull-down pattern).
Touch
167
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
Samsung Galaxy S24+ (Exynos)
How Display Touch score is composed
To evaluate touch, DXOMARK uses a touch robot and a high-speed camera to play and record a set of scenarios for smoothness, accuracy and response-time evaluation.
Average Touch Response Time Huawei Mate 60 Pro
This response time test precisely evaluates the time elapsed between a single touch of the robot on the screen and the displayed action. This test is applied to activities that require high reactivity, such as gaming.
Artifacts
123
OnePlus Open
OnePlus Open
How Display Artifacts score is composed
Evaluating artifacts means checking for the performance, image rendering and motion flaws that can affect the end-user experience. DXOMARK measures precisely the device’s reflectance and the presence of flicker, and assesses the impact of residual aliasing when playing video games, among other characteristics.
Average Reflectance (SCI) Huawei Mate 60 Pro
SCI stands for Specular Component Included, which measures both the diffuse reflection and the specular reflection. Reflection from a simple glass sheet is around 4%, while it reaches about 6% for a plastic sheet. Although smartphones’ first surface is made of glass, their total reflection (without coating) is usually around 5% due to multiple reflections created by the complex optical stack.
Reflectance (SCI)
Measurements above show the reflection of the device within the visible spectrum range (400 nm to 700 nm). It includes both diffuse and specular reflection.
PWM Frequency Huawei Mate 60 Pro
1440 Hz
Bad
Good
Bad
Great
Pulse width modulation is a modulation technique that generates variable-width pulses to represent the amplitude of an analog input signal. This measurement is important for comfort because flickering at low frequencies can be perceived by some individuals, and in the most extreme cases, can induce seizures. Some experiments show that discomfort can appear at a higher frequency. A high PWM frequency (>1500 Hz) tends to be less disturbing for users.
Temporal Light Modulation
This graph represents the frequencies of lighting variation; the highest peak gives the main flicker frequency. The combination of a low frequency and a high peak is susceptible to inducing eye fatigue. Displays flicker for 2 main reasons: refresh rate and Pulse Width Modulation. This measurement is important for comfort because flickering at low frequencies can be perceived by some individuals, and in the most extreme cases, can induce seizures. Some experiments show that discomfort can appear at a higher frequency. A high PWM frequency (>1500 Hz) tends to be safer for users.
Aliasing (closeup)
Huawei Mate 60 Pro
(Photo for illustration only)
 Huawei Mate 60 Pro
Huawei Mate 60 Pro


 27th
27th
 23rd
23rd

















DXOMARK encourages its readers to share comments on the articles. To read or post comments, Disqus cookies are required. Change your Cookies Preferences and read more about our Comment Policy.