Appearing on the market in October 2020, the Pixel 5 is Google’s latest top-of-the-line smartphone. It is dust- and water-resistant, encased in Gorilla Glass 5, equipped with a Qualcomm Snapdragon 765G processor, and runs Android 11. Let’s take a look at how well it performed in our Display protocol tests.
Key display specifications:
- OLED screen
- Size: 6.0 inches (~86% screen-to-body ratio)
- Dimensions: 144.7 x 70.4 x 8 mm (5.70 x 2.77 x 0.31 inches)
- Resolution: 1080 x 2340 pixels
- Aspect ratio: 19.5:9, ~432 ppi
- Refresh rate: 90 Hz
About DXOMARK Display tests: For scoring and analysis in our smartphone and other display reviews, DXOMARK engineers perform a variety of objective and perceptual tests under controlled lab and real-life conditions. This article highlights the most important results of our testing. Note that we evaluate display attributes using only the device’s built-in display hardware and its still image (gallery) and video apps at their default settings. (For in-depth information about how we evaluate smartphone and other displays, check out our articles, “How DXOMARK tests display quality” and “A closer look at DXOMARK Display testing.”)
Test summary


The Google Pixel 5’s overall score of 74 places it among the second-tier devices in our Display protocol database. Hampered by lackluster performances in readability and video, its relatively strong showings in color, motion, and touch were not enough to lift it into better company.

Readability
Google Pixel 5
58
76
DXOMARK uses the device’s gallery app to show static (still image) content when measuring the device’s display for brightness, contrast, gamma, and blue light impact, etc.
Readability—being able to easily see content in different ambient light conditions—is arguably the most important aspect of a display, and it is precisely in this category where the Pixel 5 stumbles, as its score of 58 attests. Its peak luminance was particularly low, particularly when compared with the Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos), as shown in the graph below:
The comparison shots below illustrate low readability outdoors in shade:

The Google Pixel 5 is quick to react to rising light levels, but slow to respond to falling light conditions; further, it shows distinct steps during transitions. On the plus side, while the Pixel 5 loses brightness and contrast when viewed at angle (as all phones do to some extent), it is still readable.
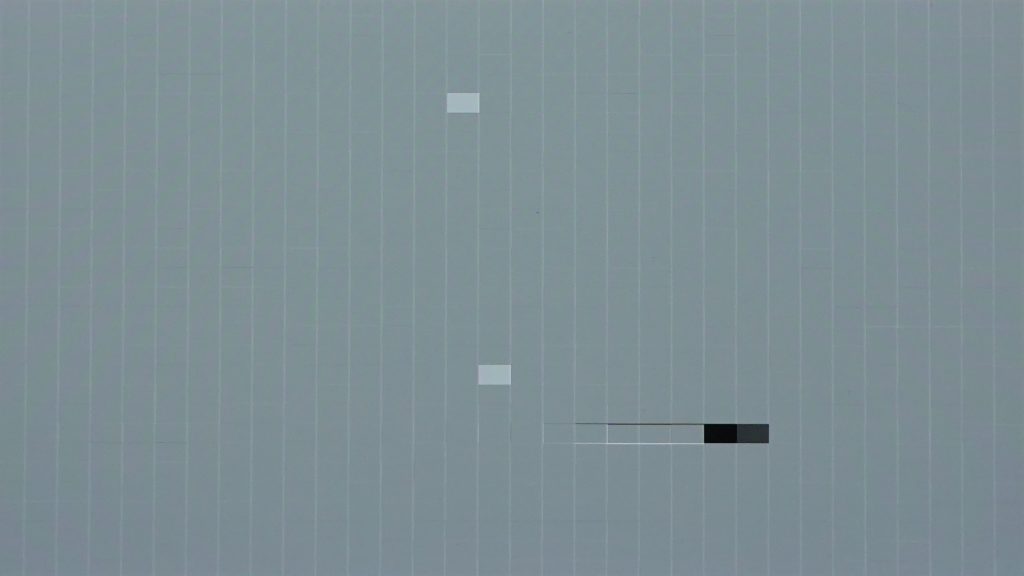
As for brightness uniformity, the device shows a brighter area at the top of the screen and a darker area at the bottom of the screen. Measured using a 20% gray pattern and a Radiant camera in dark (0 lux) conditions, the resulting color map below shows a difference in luminance from the top (right side in landscape mode) to the bottom:
The Google device appropriately adapts its brightness to respond to nighttime conditions both with and without the blue light filter (BLF) on.

Color
Google Pixel 5
79
92
DXOMARK uses the device’s gallery app to show static (still image) content when measuring the device’s display for white point, gamut, uniformity, color fidelity, and blue light filter impact, etc.
At 79 points, the Google Pixel 5 puts in a respectable if not stellar performance for Color. The charts below show its coverage for the sRGB gamut:
Our engineers did not see any color adaptation when the ambient illuminant changes. Indoors, a greenish-yellow cast is visible…
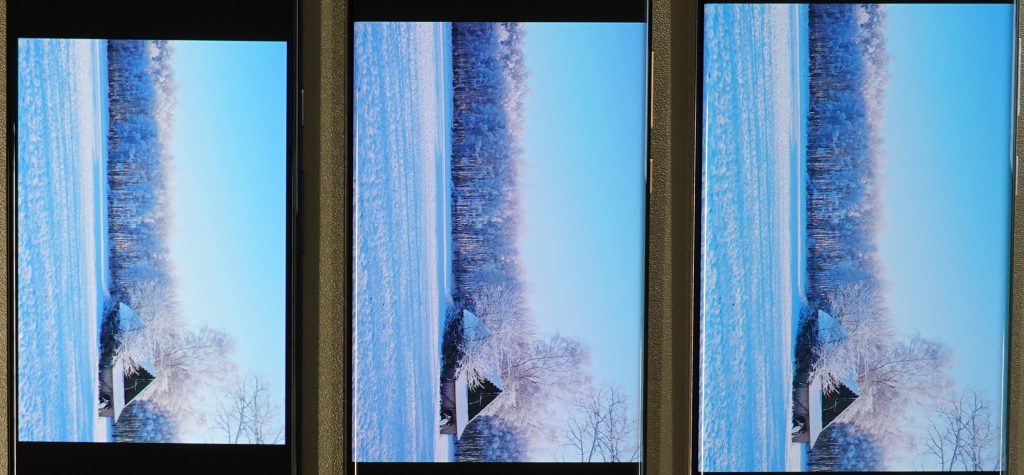

…which only becomes more pronounced in outdoor photos. Under direct sunlight, its boosting of brightness to enhance the image strongly alters the rendering, leading to inaccurate colors.

As is typical of smartphone displays generally, the Google Pixel 5 shifts color when viewed at an angle, with a blue cast appearing as well as a slight loss of saturation. More serious is the device’s color non-uniformity (which goes along with the brightness non-uniformity mentioned above): a strong color gradient is visible from top to bottom on the Google device (below left), along with a very noticeable greenish area at the top of the screen.
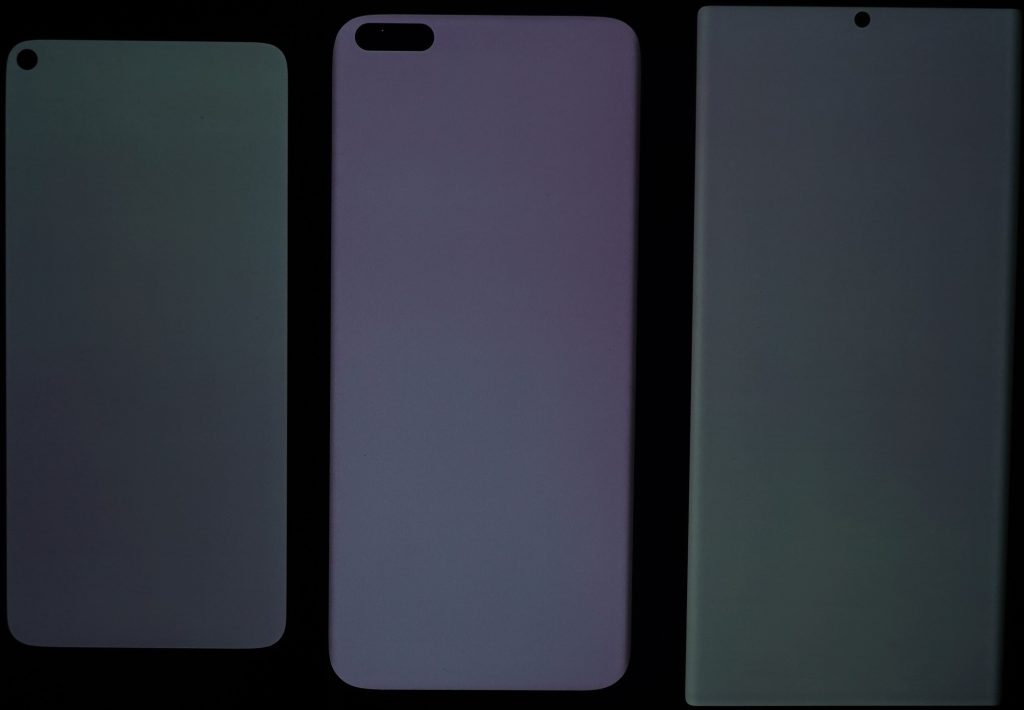

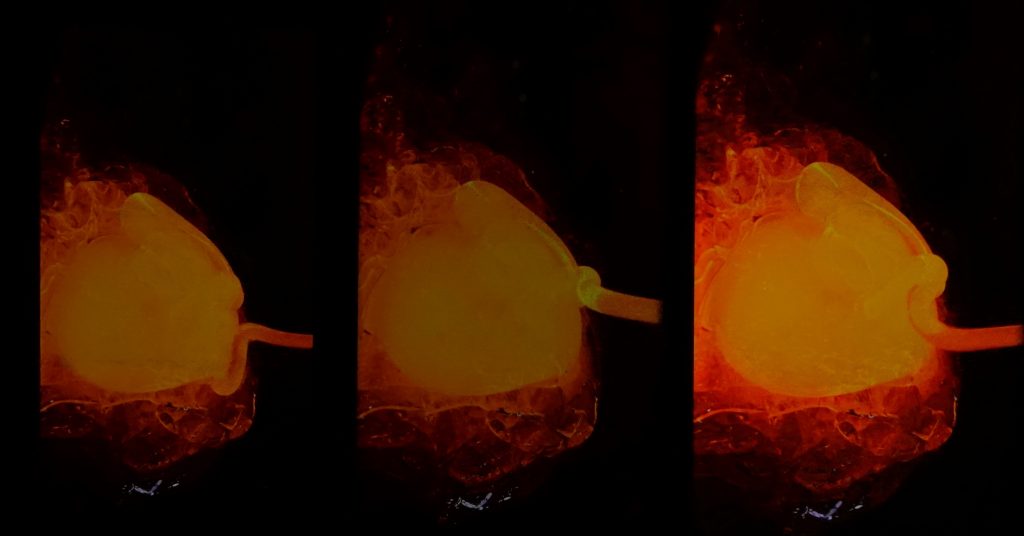
All that said, however, one of the Pixel 5’s most readily noticeable issues with color is its strong red-orange cast when the blue light filter (BLF) is on, which reduces its contrast and thus impairs readability:
BLF on, from left to right: Google Pixel 5, Huawei P40 Pro, Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)

Video
Google Pixel 5
56
91
DXOMARK uses the device’s video (or browser) app to show dynamic content when measuring the device’s display for brightness, contrast, gamma, and color.
As for Video, its score of 56 is based on our tests that show that target brightness is a bit low to be able to fully appreciate HDR10 content in particular:
Video contrast, from left to right: Google Pixel 5, Huawei P40 Pro, Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)
In addition, a green color cast is visible, along with a lack of saturation in skin tone rendering when playing HDR10 content.
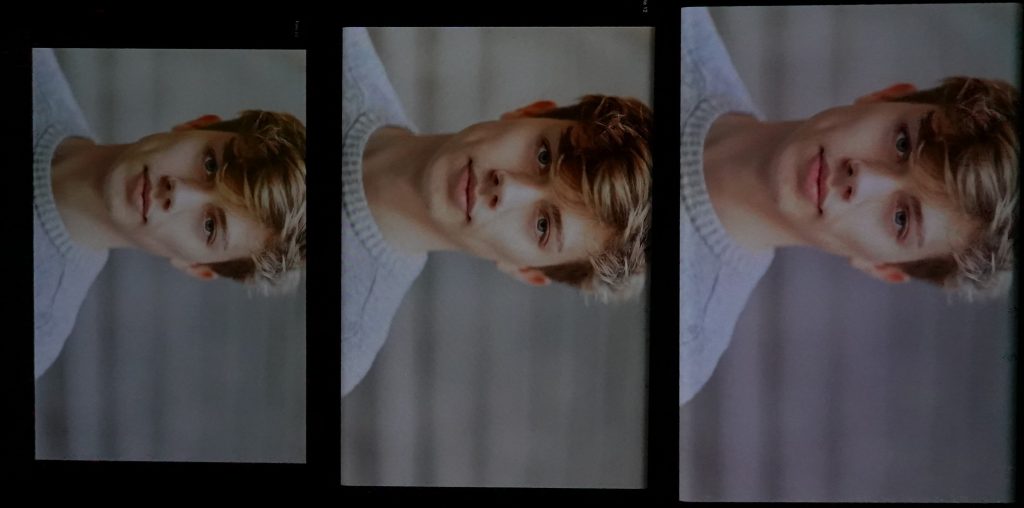

Video skin tone rendering, from left to right: Google Pixel 5, Huawei P40 Pro, Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G (Exynos)

Motion
Google Pixel 5
78
87
On the plus side, 78 is a good score for Motion — not too far away from the category-leading Huawei P40 Pro at 87 —and provides a needed boost to the Pixel 5’s overall score. The device shows a couple of stutters at 30 fps (below left), but our testers only rarely observed frame drops at 60 fps (below right):

Stutters were clearly visible when playing video games. As for motion blur, the device shows some duplications but appears sharp. The most serious problem we observed was that after the user rewinds during playback, the Pixel 5 pauses before resuming the video — and the larger the video file size, the longer the pause.

Touch
Google Pixel 5
70
85
Touch on the Pixel 5 is quite accurate when zooming in the gallery app; however, pinch-zooming is capped— that is, you cannot use the gesture to zoom in to the phone’s maximum magnification.

That said, the Google device is quite smooth in the gallery app or when browsing, but its performance deteriorated when gaming, otherwise its score of 70 would have been higher.

Artifacts
Google Pixel 5
76
86
The Google Pixel 5’s mean reflectance is a very good 4.66%; the graph below shows its reflectance curve over the visible spectrum:
The Google Pixel 5 scored 76 points in our Artifacts category. Although its notch is small, it nonetheless covers a part of the screen and thus can be disturbing during full-screen activities. Flicker, however, is not a problem:
Further, the Google device shows no judder at 24, 30, or 60 fps. While ghost touches do occasionally occur, its biggest problem is with aliasing, which is quite visible when gaming:
Conclusion
Despite good handling of color and motion, and decent control of touch, display performance on the Google Pixel 5 is unfortunately something of a disappointment overall, with improvements to readability, video, and artifacts necessary to challenge the competition.
Pros
- Device adapts to ambient light at night; image enhancements boost readability in direct sunlight.
- The touch is accurate on every part of the display and is also fluid when browsing or in the gallery app.
- The device shows almost no frame drops when watching video; judder is also well managed.
Cons
- Light levels are too low in general (except in low light), and readability enhancement under sunlight alters image colors.
- Low luminance and contrast impact the user experience when watching videos.
- The device stutters regularly when playing video games.
- Falling light transitions are slow and show steps.




DXOMARK encourages its readers to share comments on the articles. To read or post comments, Disqus cookies are required. Change your Cookies Preferences and read more about our Comment Policy.